Thyroid Disorders: Treatment Overview
June 28, 2022Thyroid disorders, like hyper- and hypothyroidism, are much more common than you would expect. Treating thyroid disorders is important, if they go untreated they can cause further health complications.
The Inside Rx Blog
Get the Inside Scoop on tips & tricks that may help your family save on prescriptions!
Subscribe to stay up to date with the latest news and tips
Reviewed by the Office of Clinical Evaluation and Policy (OCEP), Evernorth
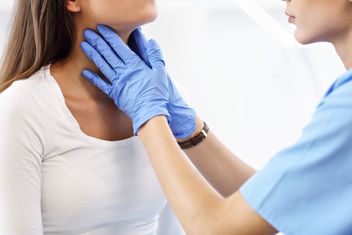
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland that wraps around the windpipe (trachea). It is responsible for making certain hormones involved with vital functions in the body, such as digestion, growth, and heart rate. Problems with the thyroid can lead to abnormal thyroid hormone levels and health complications.
Around 20 million people are reported to have some type of thyroid disorder, such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Symptoms can vary depending on the type of thyroid disorder, and thyroid disorders are often diagnosed through measuring thyroid hormone levels. Medication is usually the treatment of choice for thyroid disorders. Surgery may be recommended depending on the type of disorder.
Continue reading to learn more about treatments for thyroid disorders.
Medications
Thyroid hormone replacement medications
Certain drugs can be used to replace thyroid hormones in people with hypothyroidism, a disorder in which the thyroid doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include extreme fatigue, depression, forgetfulness, and some weight gain.
Levothyroxine (Synthroid®) is one of the most commonly prescribed thyroid replacement medications that contain a manufactured or synthetic version of thyroxine (T4). Liothyronine (Cytomel®) contains a synthetic version of triiodothyronine (T3). Some healthcare providers may prescribe Armour Thyroid, which is natural preparation derived from porcine (pig) thyroid glands and contains a combination of T4 and T3.
Antithyroid agents
Antithyroid agents are used to treat hyperthyroidism, a disorder in which the thyroid makes too much thyroid hormone. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include irritability, nervousness, muscle weakness, unexplained weight loss, sleep disturbances, vision problems and eye irritation. Antithyroid agents help block the production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid. Currently, there are two antithyroid agents available in the U.S. called methimazole and propylthiouracil.
Radioactive iodine
People with hyperthyroidism may need to take radioactive iodine. Taken orally, radioactive iodine is absorbed into the thyroid gland. It then causes the thyroid gland to shrink and stop producing thyroid hormones. After radioactive iodine therapy, it may be necessary to take thyroid replacement medications for life.
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers may be used to help alleviate the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as a rapid heart rate and nervousness. While they don’t stop the production of thyroid hormones, beta-blockers help counteract the effects of high levels of thyroid hormones in the body. These medications may be used in addition to other drugs that target the thyroid, such as antithyroid agents and radioactive iodine. Common beta-blockers include propranolol, atenolol (Tenormin®), metoprolol (Lopressor®) and nadolol (Corgard®).
Surgery
Surgery is an option for people with hyperthyroidism, an irregular growth of the thyroid gland (goiter), thyroid eye disease, Graves’ disease and thyroid cancer. Surgical procedures involve removing part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). Lifelong treatment with thyroid replacement medications is often needed after a thyroidectomy to ensure normal thyroid hormone levels in the body.
When used to treat thyroid cancer, surgery may be accompanied by radiation or chemotherapy. The treatment used for thyroid cancer will vary depending on the severity of the cancer and whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Treatment with medications is usually added after having surgery.

Vyvanse Coupon Guide 2025: How to Cut Your Prescription Costs

Chronic Kidney Disease: Warning Signs You Shouldn't Ignore

Seasonal Allergies Treatment: Simple Solutions That Bring Real Relief

Lost Your Job? Here's How to Get Prescriptions Without Insurance Today
Liothyronine Sodium
$ 11.10Metoprolol Tartrate
$ 7.62Inside Rx is here to help
Most treatments and medications for thyroid disorders are covered by health insurance plans. Copay costs can vary depending on the plan. However, if you don’t have insurance or your copay costs are high with insurance, you may want to choose other savings options.
Inside Rx provides a discount card that can help you save up to 80% on brand and generic medications. Before purchasing your treatment, you should compare the price with insurance to the price with a savings card. You may end up saving more than you would with insurance.